|
I am a Computer Vision PhD student at Australian National University (ANU), under the guidance of Dr. Chuong Nguyen and Prof. Hongdong Li. My research focuses on Generative AI, Multimodal Learning, 3D Understanding, and autonomous perception. I bring a unique hybrid background: prior to my PhD, I spent 16 years as an Embedded Software Engineer in the automotive industry, architecting real-time multimedia and navigation systems for global OEMs (Toyota/Honda). Most recently, I interned at Amazon, where I developed diffusion models for Joint Shadow Generation and Relighting, and at NVIDIA, where I researched Hallucination Mitigation for MLLMs. Email / Google Scholar / Linkedin / Github |

|
|
|

|
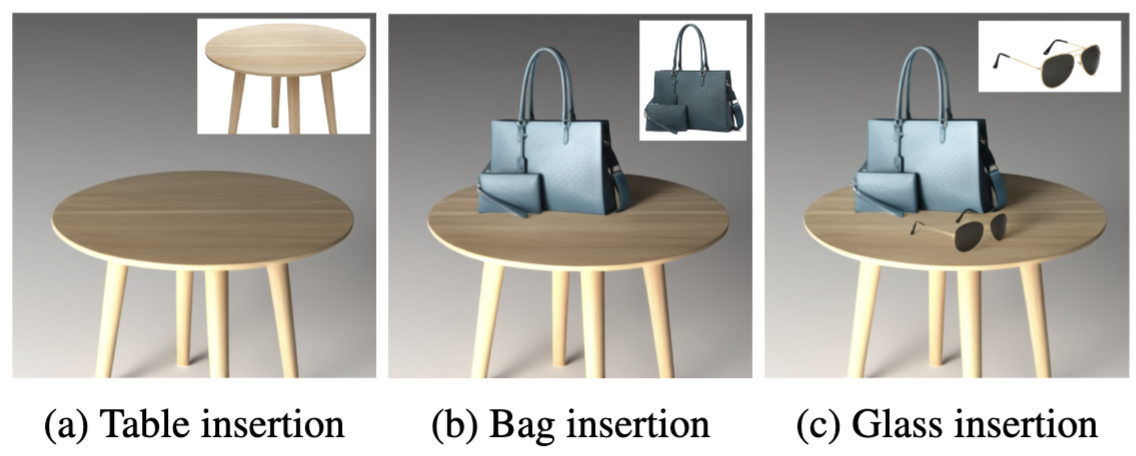
Shan Wang, Peixia Li, Chenchen Xu, Ziang Cheng, Jiayu Yang, Hongdong Li and Pulak Purkait ICLR, 2026 paper We propose Light–Geometry Interaction (LGI) maps, a novel representation that encodes light-aware occlusion from monocular depth. Unlike ray tracing, which requires full 3D reconstruction, LGI captures essential light–shadow interactions reliably and accurately, computed from off-the-shelf 2.5D depth map predictions. LGI explicitly ties illumination direction to geometry, providing a physics-inspired prior that constrains generative models. Without such prior, these models often produce floating shadows, inconsistent illumination, and implausible shadow geometry. Building on this representation, we propose a unified pipeline for joint shadow generation and relighting-unlike prior methods that treat them as disjoint tasks-capturing the intrinsic coupling of illumination and shadowing essential for modeling indirect effects. By embedding LGI into a bridge-matching generative backbone, we reduce ambiguity and enforce physically consistent light–shadow reasoning. To enable effective training, we curated the first large-scale benchmark dataset for joint shadow and relighting, covering reflections, transparency, and complex interreflections. Experiments show significant gains in realism and consistency across synthetic and real images. LGI thus bridges geometry-inspired rendering with generative modeling, enabling efficient, physically consistent shadow generation and relighting. |
|
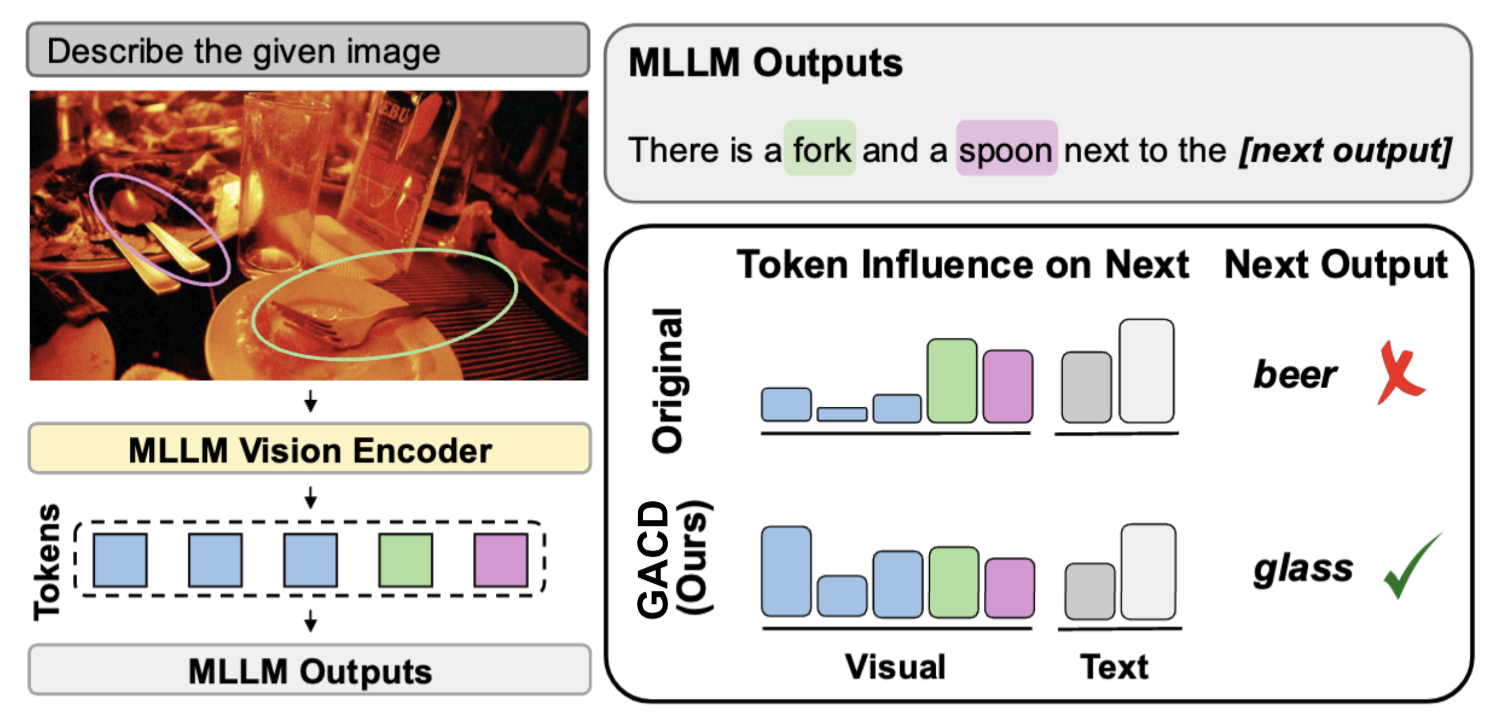
Shan Wang, Maying Shen, Nadine Chang, Chuong Nguyen, Hongdong Li and Jose M Alvarez CVPR, 2026 paper Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) achieve strong performance across diverse tasks but remain prone to hallucinations, where outputs are not grounded in visual inputs. This issue can be attributed to two main biases: text–visual bias, the overreliance on prompts and prior outputs, and co-occurrence bias, spurious correlations between frequently paired objects. We propose Gradient-based Influence-Aware Constrained Decoding (GACD), an inference-based method, that addresses both biases without auxiliary models, and is readily applicable to existing models without finetuning. The core of our approach is bias estimation, which uses first-order Taylor gradients to understand the contribution of individual tokens—visual features and text tokens—to the current output. Based on this analysis, GACD mitigates hallucinations through two components: (1) suppressing spurious visual features correlated with the output objects, and (2) rebalancing cross-modal contributions by strengthening visual features relative to text. Experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that GACD effectively reduces hallucinations and improves the visual grounding of MLLMs outputs. |

|
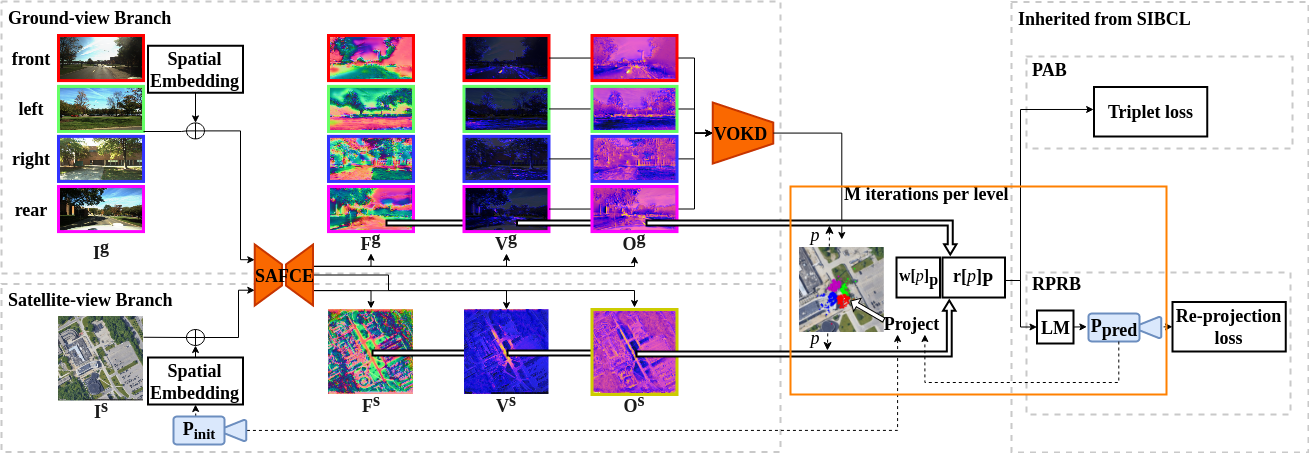
Shan Wang, Chuong Nguyen, Jiawei Liu, Yanhao Zhang, Sundaram Muthu, Fahira Afzalmaken, Kaihao Zhang and Hongdong Li CVPR, 2024 paper This paper presents a novel aerial-to-ground feature aggregation strategy, tailored for the task of cross-view image-based geo-localization. Conventional vision-based methods heavily rely on matching ground-view image features with a pre-recorded image database, often through establishing planar homography correspondences via a planar ground assumption. As such, they tend to ignore features that are off-ground and not suited for handling visual occlusions, leading to unreliable localization in challenging scenarios. WeproposeaTop-to-Ground Aggregation (T2GA)module that capitalizes aerial orthographic views to aggregate features down to the ground level, leveraging reliable off-ground information to improve feature alignment. Furthermore, we introduce a Cycle Domain Adaptation (CycDA) loss that ensures feature extraction robustness across domain changes. Additionally, an Equidistant Re-projection (ERP) loss is introduced to equalize the impact of all keypoints on orientation error, leading to a more extended distribution of keypoints, which benefits orientation estimation. On both KITTI and Ford Multi-AV datasets, our method consistently achieves the lowest mean longitudinal and lateral translations across different settings and obtains the smallest orientation error when the initial pose is less accurate, a more challenging setting. Further, it can complete an entire route through continual vehicle pose estimation with initial vehicle pose given only at the starting point. |
|
Shan Wang, Yanhao Zhang, Akhil Perincherry, Ankit Vora, and Hongdong Li ICCV, 2023 paper / project page This paper proposes a fine-grained self-localization method for outdoor robotics that utilizes a flexible number of onboard cameras and readily accessible satellite images. The proposed method addresses limitations in existing cross-view localization methods that struggle to handle noise sources such as moving objects and seasonal variations, achieving significant performance improvement. |
|
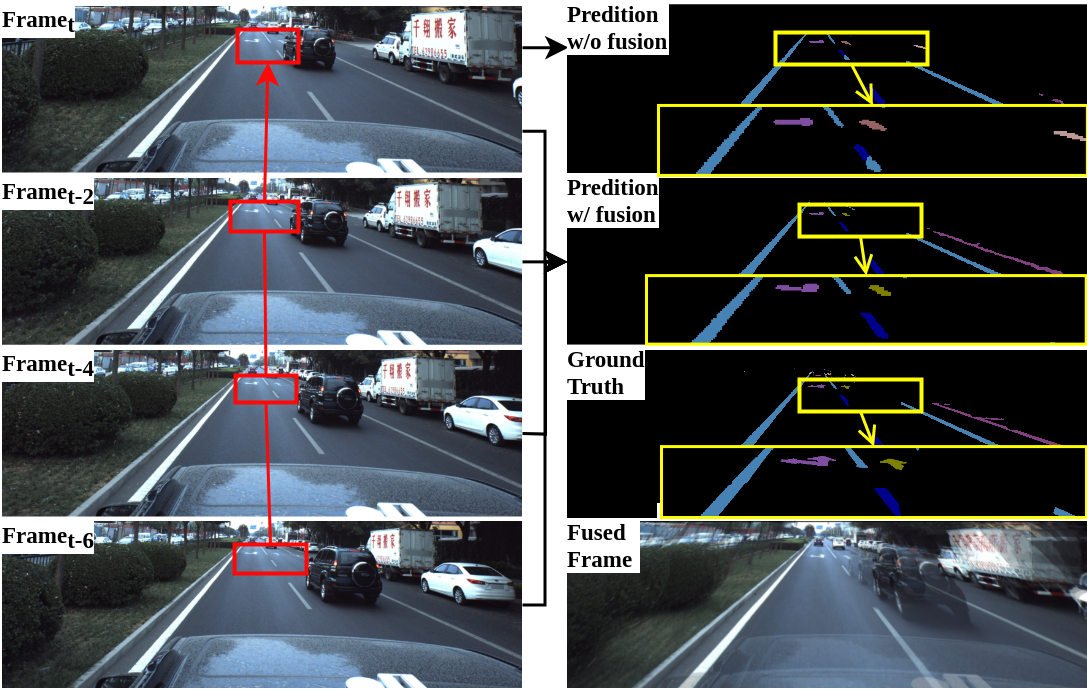
Shan Wang, Chuong Nguyen, Jiawei Liu, Kaihao Zhang, Wenhan Luo, Yanhao Zhang, Sundaram Muthu, Fahira Afzalmaken and Hongdong Li ICCV, 2023 paper / code Reliable segmentation of road lines and markings is critical to autonomous driving. Our work is motivated by the observations that road lines and markings are (1) frequently occluded in the presence of moving vehicles, shadow, and glare and (2) highly structured with low intra-class shape variance and overall high appearance consistency. To solve these issues, we propose a Homography Guided Fusion (HomoFusion) module to exploit temporally-adjacent video frames for complementary cues facilitating the correct classification of the partially occluded road lines or markings. |
|
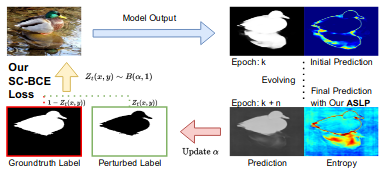
J Liu, C Ye, S Wang, R Cui, J Zhang, K Zhang, N Barnes ICCV, 2023 paper / code For safety-related applications, it is crucial to produce trustworthy deep neural networks whose prediction is associated with confidence that can represent the likelihood of correctness for subsequent decision-making. Existing dense binary classification models are prone to being over-confident. To improve model calibration, we propose Adaptive Stochastic Label Perturbation (ASLP) which learns a unique label perturbation level for each training image. |
|
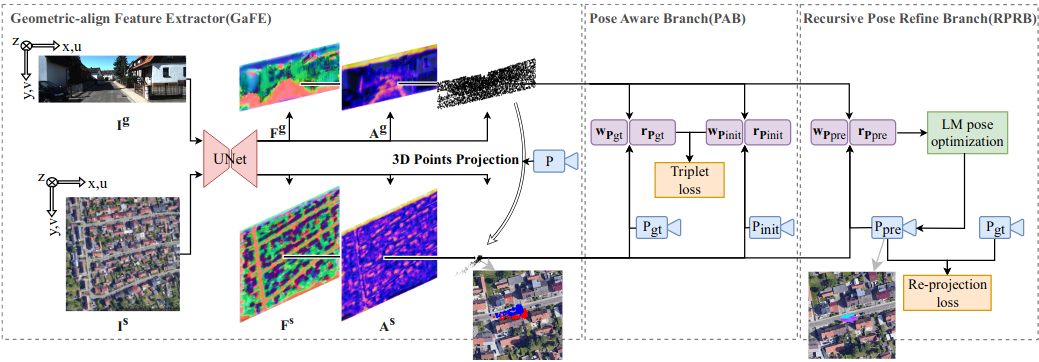
Shan Wang, Yanhao Zhang, Ankit Vora, Akhil Perincherry, and Hongdong Li ICRA, 2023 paper / project page Existing spatial localization techniques for autonomous vehicles mostly use a pre-built 3D-HD map, often constructed using a survey-grade 3D mapping vehicle, which is not only expensive but also laborious. This paper shows that by using an off-the-shelf high-definition satellite image as a ready-to-use map, we are able to achieve cross-view vehicle localization up to a satisfactory accuracy, providing a cheaper and more practical way for localization. Our method is validated on KITTI and Ford Multi-AV Seasonal datasets as ground view and Google Maps as the satellite view. The results demonstrate the superiority of our method in cross-view localization with median spatial and angular errors within 1 meter and 1∘, respectively. |
|
|
Yujiao Shi, Xin Yu, Shan Wang, and Hongdong Li ACCV, 2022 paper / code This work addresses city-scale satellite image-based camera localization by using a sequence of ground-view images. |